Regulations on Construction and Material Handling
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Construction |
| ✅ Wordcount: 3764 words | ✅ Published: 03 Nov 2020 |
LO 1:
The law says that the area of your construction site must be held in ‘ good order ‘ as well as every place of work must be kept clean. The purpose of this is to maintain what is generally called a reasonable ‘housekeeping’ standard around the site. Furthermore, under HASAWA (Health and Safety at Work Act 1974) all contractors must plan and control their work in such a manner that is performed safely and without health risks to themselves or others around them.
Materials storage
Safe and efficient storage of materials depends on good communication and collaboration among all involved including clients, contractors, suppliers and tradesmen. The arrangements for storage of materials should be discussed on all projects and agreed by contractors and the client. Larger notifiable projects should have material storage arrangements included in the Construction phase plan. Some tips for materials storage on site include:
- Designated storage areas
- Segregated pedestrian routes, that should be kept clean and without materials obstructing the access routes that could cause a slips or trips.
- Flammable materials stored away from other materials
- If materials are to be stored on height, it is necessary to put a guard rails so people don’t fall when stacking or collecting the materials.
- Keep the amount of materials on site to a minimum by planning the deliveries.
Lifting and manual handling
Incorrect manual handling is one of the most common causes of work-related injury. Bad posture when lifting or carrying heavy material can cause musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). Therefore, the risks from manual handling should be carefully considered into a risk assessment. Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 provides guidance on how to avoid, assess and reduce the risk of injury from manual handling.
Design management Regulations
The Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015
The purpose of CDM Regulations is to ensure that health and safety issues are adequately considered during the development of a project, thus reducing the risk of harm to those who have to build, use and maintain structures. They were developed from a European directive that had looked at the primary cause of accidents. The study has indicated that a third of accidents could be prevented during the early design stage of the project. Thus, the designers now have to undertake risk assessments, so that the client and the constructors are aware of the associated risks.
Risk assessments and method statements (RAMS)
The general purpose of RAMS is to eliminate or reduce and manage the risks involved in carrying out construction works. While the particular process of conducting a formal risk assessment is not a requirement of the CDM Regs, Regulation 3(6)(a) of the Health and Safety at Work Regulations requires that workplace risks are adequately controlled. This involves considering what could harm people and deciding what steps need to taken to prevent that harm. Risk assessment can be very uncomplicated process that doesn’t require complicated techniques and can be performed by a non-specialist person. This method is commonly referred to as a qualitative risk assessment. On the other hand, if the job involves works with a chemical or nuclear plants, approaches such as quantitative risk assessment may be required. The quantitative risk assessment is sometimes known as a numerical estimate of the probability that a harm will result from the occurrence of certain event.
Method statements are commonly used as a means of controlling particular health and safety risks found (usually after the preparation of a risk assessment) such as; lifting operations, demolition or working at height and etc. The method statement assists in managing the work and ensures that the proper control measures have been communicated to those involved. Method statements don’t need to be unnecessarily long to be effective. They should be easy to understand by the people who are going to do the work and they should not be overcomplicated and sometimes they might be illustrated if necessary.
Control of Substances Hazardous to Health 2002 (COSHH)
Many processes in the construction industry involve the use of substances which could be harmful to health. COSHH Regs 2002 state that employers must prevent or reduce employees’ exposure to substances, such as chemicals, fumes, dusts and etc. There are wide variety of situations in which employees could be exposed to substances that are harmful to their health. For example, concrete is one of the highly hazardous materials because it could be harmful for the interior and the exterior of humans. Contact with the concrete without the relevant Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) can cause dermatitis and skin problems or if the worker breaths in the cement dust, he/she can caught a respiratory disease and damage their lungs. That’s why it is important to use the necessary PPE for the relevant job. The main PPE consists of safety boots, safety clothing, gloves, glasses and mask. Every substance that is harmful in any manner will have a COSHH label on it as part of the regulation and will express exactly what it is.

Figure 1 : COSHH labels (RospaTraining, 2013)
Working in confined spaces
The biggest danger of working in the confined spaces is that those are restricted to natural ventilation. Most common confined spaces in construction are basements and under-floor spaces. When working in confined spaces emergency arrangements in event of an accident should always be considered. As well as, risk assessment for the people who will have to enter the confined space should a rescue be required and available personnel who are trained to remove unconscious operatives from the confined space. The relevant regulation that apply to this type of works is Confined Spaces Regulations 1997.
Working at Height Regulations 2005
The purpose of these regulations is to control the large number of fatalities that are caused by a fall from height. These Regulations apply to employers who contract others to work at height and they must ensure that the work is properly planned and carried out by trained people. This involves providing the workers with the right type of equipment for working at height. There are many other factors that need to be considered when working at height, including:
- Weather conditions
- Check if the place is safe before the work commences
- Ensure that materials are stored safely and there is no risk of materials falling and injure somebody working underneath
- Plan for emergencies and evacuation
LO 2:
Material Environmental profiling and lifecycle assessment
The BRE Environmental Profiles Methodology is a method for defining and assessing the environmental effects of construction materials during their lifecycle from cradle-to-grave. This includes all the stages of its life from extraction to disposal and focuses on the four main processes:
- ISO 14040 and 14044 – extraction of the material
- ISO 14025 – processing
- EN 15804 – how the material will be material used
- EN 15978 – where the material will be used and how it will be disposed
Environmental profiles enable specifiers to determine accurate and comparable environmental information on competitive building materials. This certification on the manufacturer’s product means that the environmental performance will be as specified. It is a huge benefit for the designers because it is much easier for them to choose the most reliable building materials.
Lifecycle assessment
A life cycle assessment is performed to determine the likely environmental impacts of the materials, services and products used for the duration of the defined lifecycle. The energy and materials used, together with waste and pollutants produced as a result of a product or activity, are quantified in a full LCA over the entire life cycle. Companies carry out LCA to identify the environmental impact and cost savings of their products.
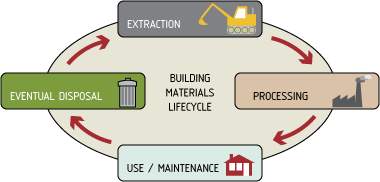
Figure 2: LCA process
Plastic could be an example of a material that would be carried out through a LCA. Plastics are derived from natural, organic materials such as cellulose, coal, natural gas, salt and crude oil. The production begins with crude oil distillation in an oil refinery. Plastics are manufactured using two primary processes-polymerization and polycondensation-and both require specific catalysts. Plastics play a major role in the sustainable construction and it is the second largest consumer of plastics after retail. Plastics in construction can often be seen in the form of PVC windows, plastic water pipes, plastic foam insulation and many more. Plastic foams offer excellent insulating properties and are extremely cost efficient. Plastic pipes require less energy to produce (embodied energy) than concrete or iron, and also save on transport costs and pollution in the construction industry since they are lightweight. In fact, replacing Victorian pipes in London with new plastic pipes will decrease leakage and could save large amounts of water, as well as the consequent energy saving needed to process and pump the water.
Waste management
Plastics recycling is taking place on a significant scale in the UK and extensive research is being carried out to find the most efficient methods of recycling. Raw materials are valuable resource, so the industry makes an attempts to recycle as much as possible and save both resources and the environment. There are two main methods for plastics recycling:
- The simplest method of plastics recycling is Mechanical recycling. This is where the plastics are softened by heating, so their form can be changed easily by using moulding granules to produce new products. The process involves gathering, sorting baling and then reducing the size into flakes or granules that may need washing and drying afterwards. This is then recompounded with chemicals and/or more raw material, until extruded and sliced into ready-to-use pellets.
- The other method is known as Feedstock recycling. It involves breaking down polymers by using heat or pressure to their component parts. Such pieces can be used in order to produce new plastic materials and chemicals. The main benefit of Feedstock recycling is when the materials are mixed or polluted.
Benefits of product declaration and environmental certification
An environmental product declaration (EPD) is a document that may be used in different countries to illustrate a product’s environmental performance in a quantifiable way. EN 15804 stands for The European Standard for the generation of environmental product declarations for construction products. Environmental Product Declarations are created on the basis of data obtained through LCA. EPD may be used externally for commercial purposes and internally for enhancement of the manufacture of the product or the efficiency of the process. According to the international standard ISO 21930 (2007) on environmental declaration of building products, EPD’s overall objective is to encourage the demand and supply of building products which cause less stress on the environment by providing verifiable and accurate information on environmental aspects of building products which is not misleading, thereby stimulating the continuous environmental improvement.
EPD provides information such as:
- Reliable data and information on a product or material’s environmental impact over a part or all of its life cycle.
- Transparency in reporting on topics such as environment health and safety, durability usage criteria and acceptable forms of recycling or disposal.
- Verification by third parties that the data were produced according to appropriate regulations and international standards. Construction products EPD standards include ISO 14025 (2006) and European standard EN 15804 (2013)
- A base for continuous improvement measurements. EPD-publishing manufacturers can demonstrate product integrity in terms of environmental performance and are likely to become more inspired towards constant improvement.
- An incentive for developer companies to direct the production of PCRs
Benefits of EPD include:
- Identification of cost savings: With predictions of increasing and more unpredictable energy and resource prices, suppliers use methods such as (LCA) that measure resource and energy use across their goods ‘ value chain will be better positioned to explore alternative approaches and solutions that can contribute to cost savings and decreased exposure to these trends
- Meeting customer needs: When corporate customers continually establish their corporate social responsibility and priorities and environmental strategies, suppliers who use LCA and publish EPD convey their own dedication to reporting and constant improvement, creating a framework for collaboration with specifiers, designers and customers
- Ensuring the products are evaluated on a level playing field: suppliers releasing EPD for their products should guarantee that the evidence used to reflect the environmental performance of the product is reliable, relevant and reflective.
- Rising recognition in building environmental rating tools: developing global environmental rating tools is gradually identifying building products with an EPD, providing an opportunity to design teams to integrate products with EPD.
- Building Information Modelling (BIM): Potential demand for streamlined implementation and use of BIM provides additional opportunities to whole-build whole-of-life evaluation.
EPD (Branz,n.d.)
LO 3:
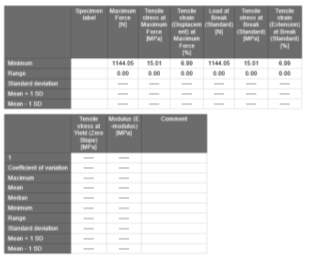
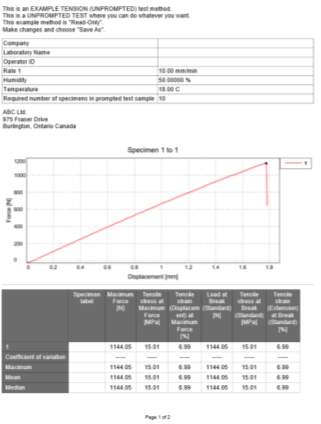

Results of testing procedure




I have carried out a tensile strength (elongation) test on two polymer materials using a tensile testing machine. The two graphs above show the different displacement results of both materials being put under pulling tension. Significant difference can be seen in the force applied. The first specimen force ascended slower than the second one, hence giving us the different results. The purpose of the test was to determine how much these two certain materials can stretch before they break.
The results obtained from the tests of both materials give us information such as Maximum force, Tensile strength at maximum force, Tensile strain (Displacement) at maximum force, Load at break, Tensile stress at break, Tensile strain (Extension) at break and Tensile stress at Yield. The maximum force applied to the first specimen was 800.89N and this was the moment that the slope at yield occurred. On the other hand, with the specimen Nr.2 the maximum force applied was 1144.05N and this was the point of break for that material with a displacement of nearly 1.8mm, whilst on the first specimen the load at break was 574.76N but that just weakened the tensile strength of the material. This tells us that specimen Nr.2 is much more brittle than Nr.1 because it broke only with little elastic deformation and without visible plastic deformation, whilst Nr.1 showed that it has high elasticity because it reached approx. 62mm Displacement without breaking completely and the tensile strain at maximum force reached 42.95%. It was unexpected that the specimen Nr.1 had the applied force of 800.89N and did not break, instead it just stretched in the middle as shown on the picture above.
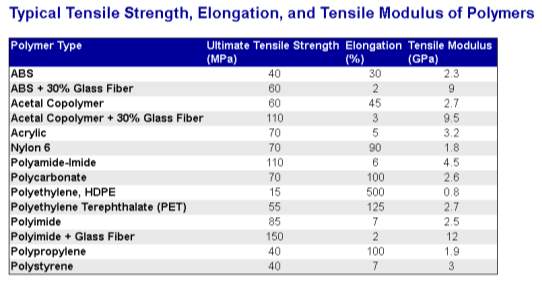
Figure 3: Mattweb (2019)
The table above shows the typical data on ultimate tensile strength, elongation and tensile modulus. Comparing my results to the standards given on the table, we can see that my results were irregular as they are very different from the ones shown on the table. There are many factors that could be the reason for me receiving a different from the standard results including: the specimen not properly positioned on the grips, the process of manufacture of the material e.g. the type of cutting and whether its been cut by laser or not or just a simple human error.
Performance properties of construction materials for building
Plastics
The general name Plastic refers to a wide variety of polymer based synthetic materials. Because of its versatility, strength-to-weight ratio, durability, corrosion resistance and so on, it can be used to carry on a wide range of functions in the construction industry. Plastic can be manufactured in shapes such as; pipes, cables, coverings, sheets and so on; and can be moulded or extended to produce components of low density; and dissolved into solvents or spread as emulsions. The advantages of using plastic in construction are that it is lightweight but strong, making transportation and maneuvering around sites easier. It is also resistant to corrosion, and is strongly weather-resistant because it can achieve tight seals. Additionally, plastic can be flexible and can be easily extruded, bent, moulded, etc. Also plastics can be removed easily, and some plastics can be recycled. The disadvantages of plastics are its high embodied energy and poor elasticity modulus, which implies that it is typically inappropriate for load-bearing purposes. Some plastics have environmental concerns due to recycling difficulties, persistence in the environment after disposal, and concerns about chemical additives used to make plastics flexible and fire-resistant.
Concrete
Concrete has the worldwide popularity as one of the most plenteous resources in the world. Using it is extremely versatile, as it produces stone-like material that allows for many uses. Concrete is often mistaken with cement but in fact, the concrete is made up of a combination of several materials and cement. The durability and versatility of Concrete make it a material of preference, especially useful because of low cost of maintenance and repair. Concrete is used in everyday life from commercial and residential houses, bridges and roads, supporting complex and basic structures for protection and aesthetics. Concrete has the ability to gain strength over time and help to conserve resources because of its ability to remain a high quality material with very little or no need of maintenance or repair. Concrete is one of the most durable material that exists. Additionally, the concrete is immune to rusting, burning, rotting and most of all it can provide reliable foundations for high-rise structures. Compared to other building materials such as timber, the concrete has double the lifespan of timber, which makes it suitable for long-term applications. Concrete is used for the construction of roads due to its durability which lessens the chance of potholes. Concrete is a sustainable material because it does not require much maintenance as some other building materials. The floors and walls in the houses are more solid and longer-lasting when made of concrete. Long-term projects can include both an aesthetically appealing view and safe and long-lasting structures. With the concrete’s properties the building and maintenance costs are lower. Since concrete is resistant to rot it assists in preventing allergens; it helps to avoid allergens such as pollen from entering the premises, and it helps regulate the temperature for lower costs and better energy efficiency. Concrete requires very low embodied energy to be produced, since its main component is the limestone, which is one of the most plentiful resource on Earth, offering an almost infinite source. Concrete has the thermal ability to retain and absorb heat, which helps to save on energy and costs making the building highly efficient.
Steel
Due to its proven strength and durability, Steel is one of the key materials used in the construction industry. Commercial carbon steels do not corrode at room temperature in pure, dry air, although they do in moist and contaminated environments. This might cause structural failures with a risk of safety hazards. The more recently emerged stainless steels do not corrode on their surfaces when they are at normal climatic conditions, because they contain a high amount of alloy elements such as chromium. Stainless steel is commonly used as a building material, since it has the desirable properties of the standard steel but excluding the disadvantages. For stainless steels used for engineering purposes only a few physical properties are important such as electrical and thermal conductivity and magnetic susceptibility. Stainless steel have better resistance to high temperature compared to carbon steel. The physical properties of the steel might not be the most important but they can still highly influence the selection of material. Another benefit of using steel is its resistance to fracture when small defects appear. Additionally, the steels have a small chance of failure by fatigue. The fatigue starts from the surface so it can be easily noticed while it is still in early stages so a surface treatment can be performed before the failure occurs.
Design Wiki (2019)
LO 4:
Material selection strategy based on human comforts
One of the most important considerations when designers select materials for a building is how to provide a comfortable environment to its occupants. There are many factors that can affect the human comfort in a building, that if not considered properly can lead to discomfort, or even cause ill health to people occupying it known as sick building syndrome. SBS is the term referring to symptoms of severe health and comfort consequences where no actual cause can be determined but can be related to the time spent in a particular building. Human comfort factors that designers need to consider when selecting materials for a building include:
Thermal comfort
Generally, thermal comfort refers to whether someone feels satisfied of the temperature inside a building. Poor thermal comfort would mean that the majority of the people occupying particular building feel too cold or too hot. Not only is it a potential health hazard when people are displeased with their thermal environment, it also impacts on their ability to function efficiently, i.e it might affect their productivity at work, therefore it is important to consider the thermal conductivity of the materials that make up the building.
Indoor air quality
The quality of ventilation within a building is another factor that can affect the human comfort. The purpose of the ventilation is to remove ‘stale’ air and substitute it with ‘new or fresh’ air. Humans breathe air to live but if the air is not constantly freshened, there is a risk of it getting polluted and cause people breathing it to fall ill by airborne diseases.
Visual comfort
The visual comfort of a building refers to what is aesthetically pleasing for the eyes of the occupants. It does not only refer to colour and texture of the finishing materials but also to the presence of a natural light into the premises of the building. It is proven by a study that natural light can impact on the health of the occupants. It tends to improve people’s mood and relieve stress and eyestrain. Also same as all the other factors it can improve employees and students performance. On top of that, it can drastically reduce the energy used by artificial lights.
Noise nuisance
Excessive noise is another factor that can negatively influence the human comfort. It can be prevented or reduced by selecting the right materials. The best sound insulating materials are the mass materials. Thick, dense walls provide better sound insulation than the lightweight partitions. Glass is another material that is very bad sound insulator because it is thin. It is important that any air passages around the windows are sealed tightly. Sound deadening quilts such as fiberglass quilt are ideal for sound insulation. Typically, they are used in cavity walls. Poor sound insulation can have a bad effect on people’s health or quality of life.
Reference list:
- RospaTraining (January 8, 2013) – https://rospaworkplacesafety.com/2013/01/08/what-is-coshh-about-coshh/
- LCA process (Building Research Establishment Ltd 2019) – https://www.bregroup.com/greenguide/page.jsp?id=2106
- EPD (Branz,n.d.) – https://www.branz.co.nz/epdfacts
- Mattweb (2019) – http://www.matweb.com/reference/tensilestrength.aspx
- Design Wiki (2019)
- https://www.designingbuildings.co.uk/wiki/Plastic_in_construction (11 Oct 2019)
- https://www.designingbuildings.co.uk/wiki/The_Properties_of_Concrete (13 Jan 2020)
- https://www.designingbuildings.co.uk/wiki/Stainless_steel_in_construction (02 Apr 2019)
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal



